Day 03: Assessment Form Structure
Day 3 focused on building the assessment form—the core feature that helps potential clients understand if we’re a good fit. This involved integrating React into Astro, implementing complex state management, and ensuring everything works smoothly across different user paths.
What Got Built
Today’s work centered on creating a robust, user-friendly assessment experience:
- React integration in Astro for interactive components
- Assessment.tsx component with sophisticated state management
- AssessmentQuestion.tsx for reusable question rendering
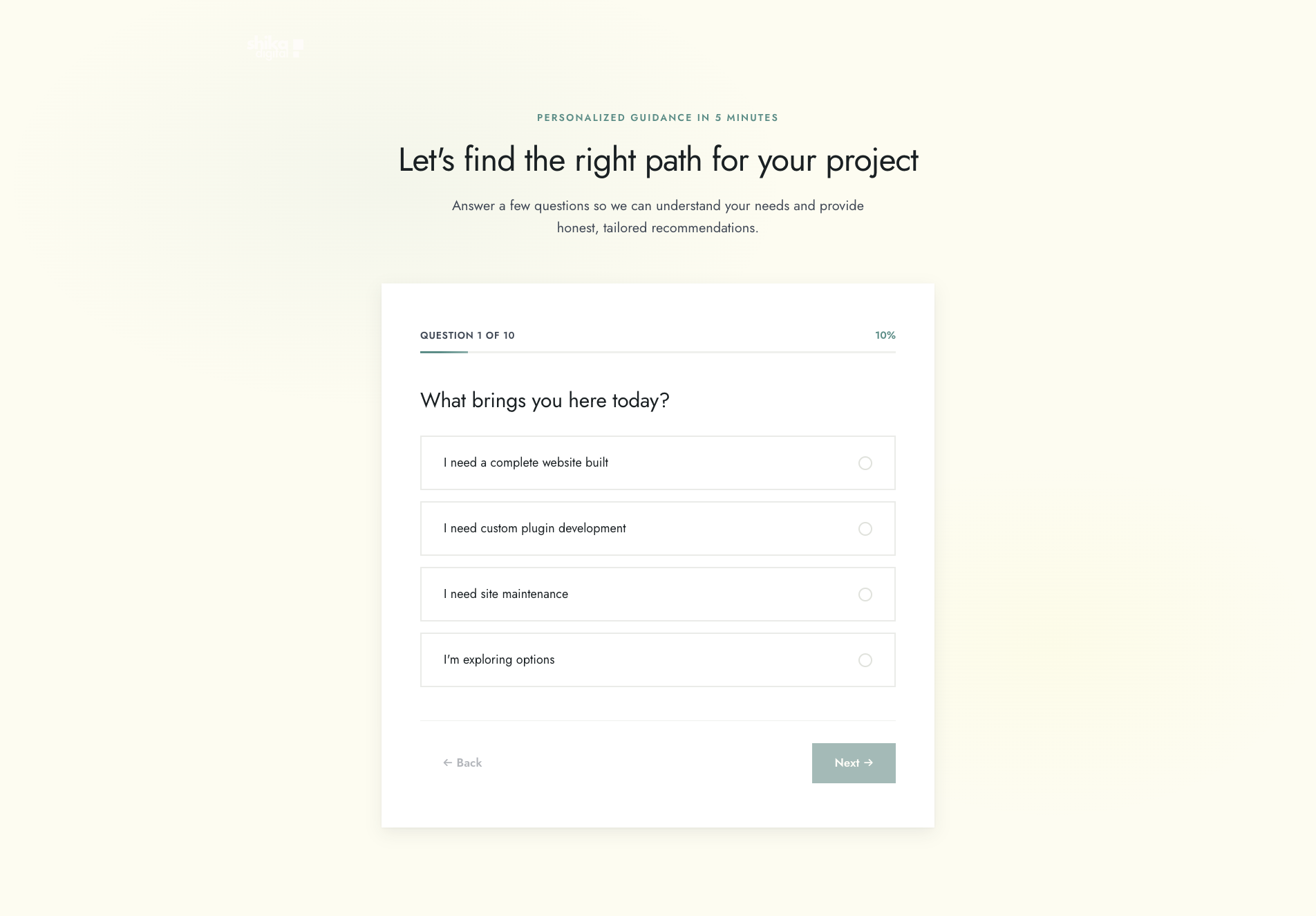
- ProgressIndicator.tsx with visual progress tracking
- Conditional question logic for three paths (Full Site, Plugin, Maintenance)
- Form validation ensuring users can’t proceed without answering
- Comprehensive test coverage for all components and logic
- Multiple refinement iterations improving UX and code quality
You can try the assessment yourself to see how it works.
The Architecture
The assessment uses a multi-step form pattern with branching logic based on the first question. Users select their project type (Full Site, Plugin, or Maintenance), which determines which subsequent questions they see.
Component Structure
// Assessment.tsx - Main orchestrator
- Manages state for all answers
- Handles navigation (Next/Back)
- Determines which questions to show based on path
- Validates answers before allowing progression
// AssessmentQuestion.tsx - Reusable question renderer
- Renders different input types (radio, checkbox, textarea)
- Handles answer selection
- Shows visual feedback for selected options
// ProgressIndicator.tsx - Visual feedback
- Shows current step and total steps
- Displays progress percentage
- Provides accessibility attributesThe Evolution: Five Iterations
Iteration 1: Basic Structure
Started with the foundation:
- Set up React integration in Astro
- Created all three components
- Implemented conditional question display
- Added all questions for each path
- Wrote initial unit tests
This got the basic functionality working but had room for improvement in styling and state management.
Iteration 2: Design System Integration
Refactored to use the design system properly:
- Added
tailwind.config.tsfor centralized configuration - Migrated hardcoded colors to CSS custom properties
- Updated all components to use CSS variables (
--color-teal,--color-black, etc.) - Improved accessibility with
focus-withinring styling - Used
accentColorproperty for consistent input theming
This made the components consistent with the rest of the site and easier to maintain.
Iteration 3: UI Polish
Enhanced the user experience:
- Replaced inline Tailwind classes with semantic CSS class names
- Added fade-in-up animation to assessment container
- Updated button labels with directional arrows (← Back, Next →)
- Changed final button from “Submit” to “View Results” for clarity
- Implemented hover effects with smooth transforms
- Added proper focus-visible states for keyboard navigation
The form now feels polished and professional, with clear visual feedback for all interactions.
Iteration 4: State Management Optimization
Improved performance and reliability:
- Consolidated multiple
setStatecalls into single updates - Refactored path determination logic to execute within state update callback
- Enhanced
canProceedvalidation to properly handle array answers - Prevented potential race conditions from sequential state updates
This made the component more efficient and eliminated potential bugs from state update timing issues.
Iteration 5: Validation Guards
Added robust validation and edge case handling:
- Added validation guard in
handleNextto prevent invalid step advancement - Implemented path change detection to clear dependent answers
- Reset progression to step 2 when user changes path selection
- Added safe value clamping in ProgressIndicator to prevent invalid states
- Prevented division by zero in progress percentage calculation
- Ensured only Q1 answer is retained when path changes
This final iteration made the form bulletproof against edge cases and user behavior that could break the flow.
Copy Text Refinements
Before Day 3, we made important copy changes to use positive, commitment-focused language:
Trust Signals:
- Changed from highlighting past problems to emphasizing our commitments
- Focused on what we do (respond, be honest, finish, communicate) rather than what others don’t do
- Removed language that could shame other developers or reinforce negative experiences
Closing CTA:
- Updated to “Ready to join the million-dollar client club?”
- Reinforced the core positioning without dwelling on past bad experiences
- Maintained warmth while staying professional
This shift in tone makes the site feel more confident and forward-looking.
Testing Strategy
Comprehensive test coverage ensures the assessment works correctly:
// Component tests
- AssessmentQuestion renders correctly for all input types
- Assessment manages state properly
- ProgressIndicator calculates percentages correctly
- Navigation buttons enable/disable appropriately
// Integration tests
- Path selection determines correct questions
- Answer validation prevents progression
- Path changes clear dependent answers
- Progress tracking updates correctlyAll tests passing with full coverage of the critical paths.
Technical Decisions
Why React in Astro?
The assessment requires complex client-side state management that’s easier to handle with React than vanilla JavaScript. Astro’s React integration makes this seamless—React components are hydrated only where needed, keeping the rest of the site static.
State Management Approach
Used React’s built-in useState rather than external state management libraries. For this use case, local component state is sufficient and keeps dependencies minimal.
Validation Strategy
Implemented validation at multiple levels:
- Input level: Disable Next button until answer provided
- Navigation level: Guard against invalid step advancement
- Path change level: Clear dependent answers to maintain consistency
This layered approach catches issues at the earliest possible point.
What I Learned
1. State management is about timing. Consolidating multiple setState calls into single updates prevents race conditions and improves performance.
2. Edge cases matter. The path change scenario (user selects Full Site, answers questions, then goes back and selects Plugin) required careful handling to maintain data consistency.
3. Semantic class names beat inline utilities. While Tailwind utilities are great for prototyping, extracting repeated patterns into semantic classes improves maintainability.
4. Positive messaging is more effective. Focusing on commitments rather than problems creates a better emotional response.
5. Iteration improves quality. Five refinement passes took the form from “working” to “polished and robust.”
Tomorrow: Assessment Completion
Day 4 will focus on:
- Implementing form submission logic
- Creating the results page routing
- Adding email notifications
- Testing the complete flow end-to-end
- Mobile responsiveness refinements
The assessment structure is solid. Time to make it functional.
This is Day 3 of 26. December 8, 2025.